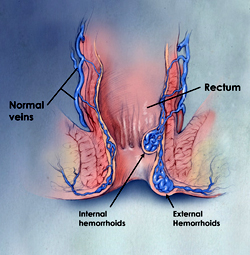
 Hemorrhoids are swollen vessels in the lower rectum and anus caused by increased pressure or straining. They are common in both men and women – especially pregnant women. After age 30, the incidence of hemorrhoids increases, and by age 50, about half of the population will have experienced them. While not life threatening, hemorrhoids can cause bleeding, burning or discomfort.
Hemorrhoids are swollen vessels in the lower rectum and anus caused by increased pressure or straining. They are common in both men and women – especially pregnant women. After age 30, the incidence of hemorrhoids increases, and by age 50, about half of the population will have experienced them. While not life threatening, hemorrhoids can cause bleeding, burning or discomfort.
For decades, chronic hemorrhoid sufferers resorted to surgery for relief. Today, a procedure called the CRH-O’Regan Disposable Hemorrhoid Banding System has all but eliminated the need for surgery and allows patients to be treated quickly and resume normal activity with very little discomfort. Most patients with office jobs find they can return to work the same day.
FAQs
The O’Regan method uses a small rubber band to strangle the base of the swollen vein, which cuts off the blood supply to the hemorrhoid. This causes the banded tissue to shrink and fall off along with the rubber band. Typically, this happens within a few days after your appointment during a routine trip to the toilet, and you may not even notice when this happens. The treatment itself takes less than five minutes and can be performed in one of our offices or endoscopy centers.
The physicians trained in this procedure tend to avoid doing more than one treatment per visit. Subsequently, some patients who have multiple hemorrhoids may require two or three treatments which are scheduled a few weeks apart.
The band placement is relatively painless due to this refined technique and it does not require anesthesia or other numbing agents. You may experience a dull ache or sense of fullness in the rectum within the first 24 hours, but this can generally be relieved by over-the-counter pain medication.
United Digestive physicians have performed thousands of rubber band ligations on patients just like you. It is the most frequently used non-surgical treatment for hemorrhoids in the world.
The CRH O’Regan method – unlike traditional banding techniques – uses a gentle suction device that reduces the risk of pain and bleeding. Some patients may have a little bleeding, discomfort and urine hesitancy, but these are considered minor complications. It’s important that you refrain from rigorous activity immediately following your treatment to reduce the risk of any complications.