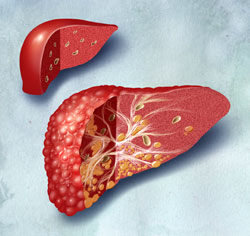
 Fatty liver is the build-up of fat in the liver cells. Although fat in the liver usually causes no damage by itself, it can be a sign of a more harmful condition. Fatty liver may be associated with or lead to inflammation of the liver, known as steatohepatitis, which can cause scarring and hardening of the liver. Extensive scarring is called cirrhosis and is considered a very serious condition.
Fatty liver is the build-up of fat in the liver cells. Although fat in the liver usually causes no damage by itself, it can be a sign of a more harmful condition. Fatty liver may be associated with or lead to inflammation of the liver, known as steatohepatitis, which can cause scarring and hardening of the liver. Extensive scarring is called cirrhosis and is considered a very serious condition.
FAQs
The liver plays an important role in breaking down fats in the body. Fat accumulates when this process malfunctions or when conditions such as diabetes mellitus, high blood triglycerides or heavy alcohol use are present. The accumulation can also be caused by tuberculosis and malnutrition, excess vitamin A or the use of certain drugs, such as valproic acids or corticosteroids. Pregnancy can also cause fatty build up.
There are usually no noticeable symptoms. In fact, fatty liver is frequently uncovered during a routine physical examination or while your physician is evaluating you for other illnesses.
To be certain of a diagnosis of fatty liver the physician may recommend a liver biopsy during which a small piece of liver tissue is removed with a needle and examined under a microscope.
Steatohepatitis, the inflammation of the liver due to fat accumulation, is one possible complication and signals serious liver damage. It occurs frequently in people who are significantly overweight or have experienced rapid weight loss.
In most instances, treatment of fatty liver and steatohepatitis requires control of the underlying conditions. This may include the reduction of high blood triglycerides, controlling diabetes or eliminating the use of alcohol. In some cases, surgical reversal of intestinal bypass for obesity is required.
If a patient is overweight, weight loss and weight control are key to successful treatment. Studies are also currently underway with drugs that may reduce liver damage in cases of steatohepatitis.
In some chronic cases involving severe liver damage, a liver transplant may be considered.
The Mediterranean diet, a primarily plant-based diet with an emphasis on vegetables, fruits, beans, nuts, whole-grains, olive oil, fish, and limited animal protein, contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory nutrients including polyphenols, fiber, and Omega-3 fatty acids which are linked to various health benefits.
Numerous evidence-based studies have been conducted over the last five decades that have shown the many positive health benefits of the Mediterranean diet, including an improvement in chronic conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and obesity.
We know sorting out a Mediterranean meal plan can be challenging, which is why we’re committed to helping simplify the process for you. We’ve partnered with ModifyHealth which offers a Mediterranean Diet meal plan program that takes all the guesswork out for you — no stressful grocery lists, ingredient-vetting or eliminating needed. Give it a try and see what switching to a Mediterranean-based diet feels like!